Water is ubiquitous on Earth—about 70 p.c of Earth’s floor is roofed by the stuff. Water is within the air, on the floor, and inside rocks. Geologic proof suggests water has been steady on Earth since about 4.3 billion years in the past.
The historical past of water on early Mars is much less sure. Figuring out when water first appeared, the place, and for the way lengthy, are all burning questions that drive Mars exploration. If Mars was as soon as liveable, some quantity of water was required.
My colleagues and I studied the mineral zircon in a meteorite from Mars and located proof that water was current when the zircon crystal shaped 4.45 billion years in the past. Our outcomes, revealed within the journal Science Advances, might symbolize the oldest proof for water on Mars.
A Moist Purple Planet
Water has lengthy been acknowledged to have performed an necessary position in early Martian historical past. To put our ends in a broader context, let’s first contemplate what “early Mars” means by way of the Martian geological timescale after which contemplate the alternative ways to search for water on Mars.
Like Earth, Mars shaped about 4.5 billion years in the past. The historical past of Mars has 4 geological intervals. These are the Amazonian (from at this time again to three billion years), the Hesperian (3 billion to three.7 billion years in the past), the Noachian (3.7 billion to 4.1 billion years in the past) and the Pre-Noachian (4.1 billion to about 4.5 billion years in the past).

Proof for water on Mars was first reported within the Seventies when NASA’s Mariner 9 spacecraft captured pictures of river valleys on the Martian floor. Later orbital missions, together with Mars World Surveyor and Mars Specific, detected the widespread presence of hydrated clay minerals on the floor. These would have wanted water.
The Martian river valleys and clay minerals are primarily present in Noachian terrains, which cowl about 45 p.c of Mars. As well as, orbiters additionally discovered massive flood channels—referred to as outflow channels—in Hesperian terrains. These counsel the short-lived presence of water on the floor, maybe from groundwater launch.
Most studies of water on Mars are in supplies or terrains older than 3 billion years. Newer than that, there isn’t a lot proof for steady liquid water on Mars.
However what about in the course of the Pre-Noachian? When did water first present up on Mars?

A Window to Pre-Noachian Mars
There are 3 ways to hunt for water on Mars. The primary is utilizing observations of the floor made by orbiting spacecraft. The second is utilizing ground-based observations corresponding to these taken by Mars rovers.
The third method is to review Martian meteorites which have landed on Earth, which is what we did.
The truth is, the one Pre-Noachian materials we now have accessible to review straight is present in meteorites from Mars. A small variety of all meteorites which have landed on Earth have come from our neighboring planet.
An excellent smaller subset of these meteorites, believed to have been ejected from Mars throughout a single asteroid influence, comprise Pre-Noachian materials.
The “poster baby” of this group is a rare rock referred to as NWA7034, or Black Magnificence.
Black Magnificence is a well-known Martian meteorite fabricated from broken-up floor materials, or regolith. Along with rock fragments, it accommodates zircons that shaped from 4.48 billion to 4.43 billion years in the past. These are the oldest items of Mars recognized.
Whereas finding out hint components in considered one of these historic zircons we discovered proof of hydrothermal processes—which means they had been uncovered to scorching water after they shaped within the distant previous.
Hint Components, Water, and a Connection to Ore Deposits
The zircon we studied is 4.45 billion years outdated. Inside it, iron, aluminum, and sodium are preserved in abundance patterns like concentric layers, much like an onion.
This sample, referred to as oscillatory zoning, signifies that incorporation of those components into the zircon occurred throughout its igneous historical past, in magma.
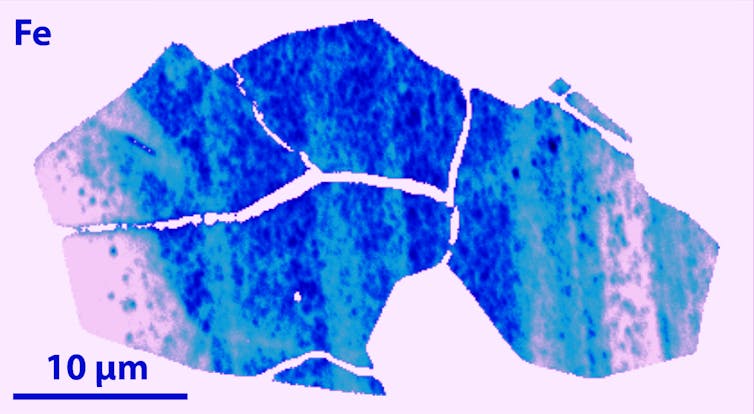
The issue is that iron, aluminum, and sodium aren’t usually present in crystalline igneous zircon—so how did these components find yourself within the Martian zircon?
The reply is scorching water.
In Earth rocks, discovering zircon with development zoning patterns for components like iron, aluminum, and sodium is uncommon. One of many solely locations the place it has been described is from Olympic Dam in South Australia, a large copper, uranium, and gold deposit.
The metals in locations like Olympic Dam had been concentrated by hydrothermal (scorching water) programs transferring by rocks throughout magmatism.
Hydrothermal programs type wherever that scorching water, heated by volcanic plumbing programs, strikes by rocks. Spectacular geysers at locations like Yellowstone Nationwide Park in the US type when hydrothermal water erupts at Earth’s floor.
Discovering a hydrothermal Martian zircon raises the intriguing risk of ore deposits forming on early Mars.
Earlier research have proposed a moist Pre-Noachian Mars. Uncommon oxygen isotope ratios in a 4.43-billion-year-old Martian zircon had been beforehand interpreted as proof for an early hydrosphere. It has even been recommended that Mars might have had an early international ocean 4.45 billion years in the past.
The large image from our examine is that magmatic hydrothermal programs had been lively in the course of the early formation of Mars’ crust 4.45 billion years in the past.
It’s not clear whether or not this implies floor water was steady presently, however we expect it’s attainable. What is obvious is that the crust of Mars, like Earth, had water shortly after it shaped—a crucial ingredient for habitability.
This text is republished from The Dialog underneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the authentic article.
Picture Credit score: JPL-Caltech/NASA

